Functions as a service (FaaS) is a great way to architect event-driven systems, whether it is in response to a RESTful HTTP event, responding to an external event, such as a content changes to a storage bucket, or a Pub/Sub message.
Cloud functions can be written in a myriad of languages, Java, Python, NodeJs to name just some, however I have chosen Java as it was a client’s first-choice in languages, and IntelliJ provides a nice debugging experience. Also I have focused on using a HTTP(S) type of trigger, though the request object that is passed for Pub/Sub or Google Cloud Storage event types are very similar, differing only in payload, and so can still be developed and debugged using the same technique.
Getting Started
The pom.xml file to provide the structure can be found
here.
In this example, we are going to implement the interface HttpFunction
com.EXAMPLE.PriceService which is mentioned in the functionTarget element of
of the pom.xml.
The interesting bits are shown below:
...
<dependencies>
<!-- Required for Function primitives -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>functions-framework-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.4</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>google-cloud-spanner</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>functions-framework-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<!--
Google Cloud Functions Framework Maven plugin
This plugin allows you to run Cloud Functions Java code
locally. Use the following terminal command to run a
given function locally:
mvn function:run -Drun.functionTarget=your.package.yourFunction
-->
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>function-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.9.7</version>
<configuration>
<functionTarget>com.EXAMPLE.PriceService</functionTarget>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Implementing the HTTP Function
The function is defined simply below:
package com.EXAMPLE;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParseException;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpFunction;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpRequest;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpResponse;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParser;
public class PriceService implements HttpFunction {
private static final Gson gson = new Gson();
@Override
public void service(HttpRequest request,
HttpResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
JsonElement parsedRequest = gson.fromJson(request.getReader(),
JsonElement.class);
if (parsedRequest == null) {
response.setStatusCode(400);
writer.write("Bad JSON format");
return;
}
if (parsedRequest != null && parsedRequest.isJsonObject()) {
JsonObject jsonObject = parsedRequest.getAsJsonObject();
String response = handleReqeust(jsonObject);
writer.write(response);
} else {
writer.write("Bad request.")
}
} catch (JsonParseException ex) {
response.setStatusCode(400);
writer.write("Parse Exception");
}
The service method takes a request and produces the response.
To make things easier, Google has defined some useful JSON parsing methods
in the package com.google.gson that helps in the mundane efforts of parsing JSON for you.
Nothing complex going on in this code, and I have omitted the part where you do
something interesting in the method handleRequest.
Debugging in IntelliJ
As indicated in the pom.xml comments, running your Cloud Function locally is
quite easy using Maven, by specifying the target:
mvn function:run -Drun.functionTarget=com.EXAMPLE.PriceService -Drun.port=8888
Here I specify the port, as the commonly used 8080 is invariably taken for some other service.
To run this in debugging-mode in IntelliJ, you simply use the Edit Configurations… menu item, and create a new maven target, filling in the parameters, as shown:
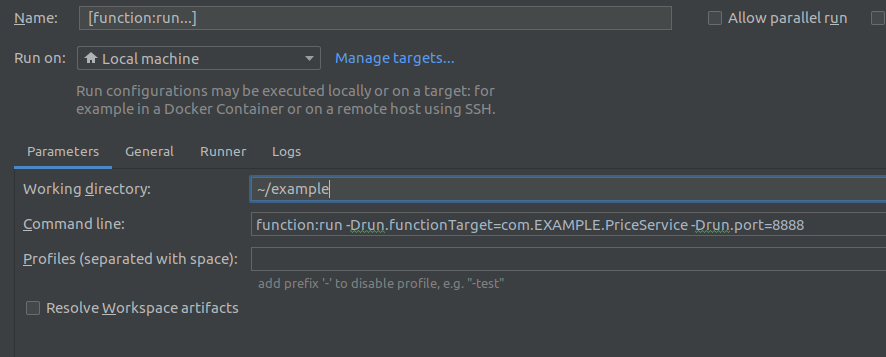
Now just put a break-point anywhere you want, prior to triggering the execution.
Triggering the function locally with Postman/Curl
To trigger the locally running cloud function, you can use Postman or Curl to author the HTTP request as:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8888' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{ "customer_pin": "452670", "item_id": "1009715"}'
Deploying to GCP
I am lazy, and so I always do this with a shell-script, so I don’t have to remember all of the parameters, and it documents itself for later.
#!/usr/bin/bash
gcloud functions deploy price-svc \
--entry-point com.EXAMPLE.PriceService \
--runtime java11 --allow-unauthenticated \
--trigger-http
This will allow unauthenticated requests. If you want to switch this to require authentication, then you also have to add additional header information with an identity-token (e.g. gcloud auth print-identity-token).
Once deployed, you can test the cloud function from the google console, that has a rudimentary testing framework.